PHP 团队于2020年11月26日宣布 PHP 8 正式发布,PHP的发展又开启了新的篇章,PHP8 引入了一些重大变更及许多新特性和性能优化机制,值得关注的改进包括以下:
- PHP 8.0 引入了备受期待的
Just In Time (JIT)编译器,能够进一步提高 PHP 脚本的执行速度 - PHP 8.0 合并了诸多性能优化
- JSON 支持现在被视为语言的核心部分,始终可用,而不是作为可选模块
- 支持 named 参数,因为它们能够指定参数名称而不是其确切顺序
- 支持类/属性/函数/方法/参数/常量的结构化元数据的属性(或在其他语言中也称为注释或修饰符)
- 支持可以指示多种不同类型的联合类型,这些类型可以用作参数或函数的返回类型
- 支持静态返回类型
-
str_contains()函数是一种检查字符串是否包含在另一个字符串中的简便方法,而不必使用strpos等。与之相似的是新的str_starts_with()和str_ends_with()函数 - 添加了
Nullsafe运算符,作为在方法上应用空合并行为的快速简便的方法 - 相比较 PHP7.4 稳定版,PHP8 在性能上大约改进了 10%,但是至少在某些方面,
JIT可以提供更多的性能。 下面我们来看看新特性和性能优化
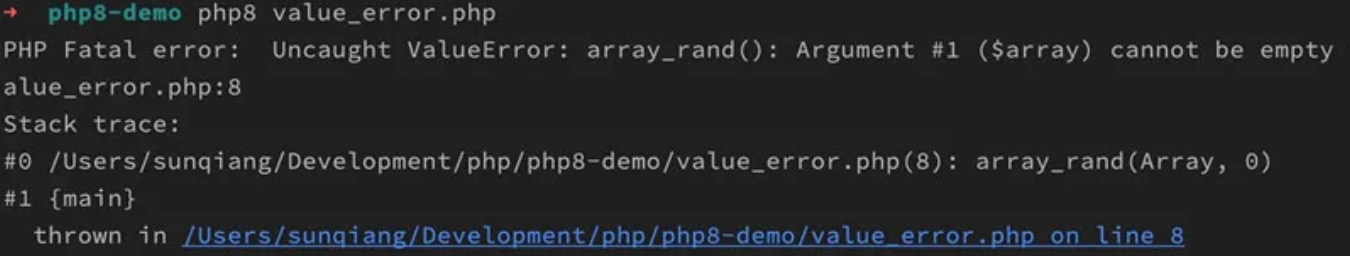
1、新增 ValueError 异常
这是 PHP8 新引入进来的 ValueError 的内置异常类,它继承自 Exception 基类。你每次传递值到函数时候,如果检测到是一个无效的类型时抛出该异常,在 PHP8 之前,这样的操作会直接做警告处理。
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
array_rand([], 0);
json_decode('{}', true, -1);
运行结果:
2、新增对联合类型的支持
PHP8 新增的联合类型,它允许一个变量拥有多个类型的值。
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
/**
* 定义一个支持联合类型的 Number 类
*/
class Number {
private int|float $number;
public function setNumber(int|float $number): void {
$this->number = $number;
}
public function getNumber(): int|float {
return $this->number;
}
}
/**
* 我们可以传递浮点型和整型值到 Number 对象
*/
$number = new Number();
$number->setNumber(5);
var_dump($number->getNumber());
$number->setNumber(11.54);
var_dump($number->getNumber());
运行结果:
int(5)
float(11.54)
3、重写方法时允许可变参数
当你在子类重写父类方法时,任何数量的参数都可以被替换成可变参数的,只要对应参数类型是兼容的就可以。
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
class A {
public function method(int $many, string $parameters, $here) {
}
}
class B extends A {
public function method(...$everything) {
var_dump($everything);
}
}
$b = new B();
$b->method('i can be overwritten!');
exit;
运行结果:
array(1) {
[0] => string(21) "i can be overwitten!"
}
4、静态返回类型
PHP8 中可以使用 static 关键字标识某个方法,且返回该方法当前所属的类,即使它是继承的,可用于后期静态绑定。
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
class Test {
public function doWhatever(): static {
// Do whatever.
return $this;
}
}
exit;
5、新增 WeakMap 特性
WeakMap 允许你创建对象到任意值的映射(这个就类似 SplObjectStorage)的同时也不会阻止作为键的对象被垃圾回收。要是某个对象键被垃圾回收了,对应键值对就会从集合中被移除。
这一新特性非常有用,开发者不必担心代码存在内存泄露了。大多数 PHP 开发者可能对此不关心,但是当你在编写长时间运行的进程时,那你就一定要提防这个问题了,比如使用 ReactPHP 进行事件驱动编程时。用了 WeakMap 后引用的对象,就会在失效时自动被垃圾回收。
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
class FooBar {
public WeakMap $cache;
public function __construct() {
$this->cache = new WeakMap();
}
public function getSomethingWithCaching(object $obj) {
return $this->cache[$obj] ??= $this->computeSomethingExpensive($obj);
}
public function computeSomethingExpensive(object $obj) {
var_dump("I got called");
return rand(1, 100);
}
}
$cacheObject = new stdClass;
$obj = new FooBar;
// "I got called" 只会打印一次
$obj->getSomethingWithCaching($cacheObject);
$obj->getSomethingWithCaching($cacheObject);
var_dump(count($obj->cache));
// 删除该对象后 WeakMap 会释放相应内存
unset($cacheObject);
var_dump(count($obj->cache));
运行结果:
string(12) "I got called"
int(1)
int(0)
6、变量语法调整
PHP8的new 和 instanceof 关键字支持用于任意表达式了
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
class Foo {}
class Bar {}
$names = ['Foo', 'Bar'];
$class = new ($names[array_rand($names)]);
var_dump($class);
运行结果:
object(Bar) #1 (0) {
}
object(Foo) #1 (0) {
}
7、对象的类名字面量
PHP8 中支持使用 $object::class 获取对象的类名,返回结果和 get_class($object) 是一样的。
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
class Test {
}
$test = new Test();
var_dump($test::class);
var_dump(get_class($test));
运行结果:
string(4) "Test"
string(4) "Test"
8、参数列表中允许出现可选的尾部逗号
和数组中的尾部逗号一样,PHP8 也支持在参数列表中定义一个尾部逗号了。
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
function method_with_many_arguments(
$a,
$b,
$c,
$d,
) {
var_dump("this is valid syntax");
}
method_with_many_arguments(
1,
2,
3,
4,
);
运行结果:
string(20) "This is valid syntax"
9、Stringable 接口
PHP8 引入了新的 Stringable 接口,只要某个类实现了 __toString 方法,就会被当作自动实现了 Stringable 接口(这一点和 Go 接口实现有些像),而不需要显式与声明实现该接口
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
class Foo {
public function __toString() {
return 'I am a class';
}
}
$obj = new Foo;
var_dump($obj instanceof Stringable);
运行结果:
bool(true)
10、throw 已经支持被用作表达式
PHP8 支持 throw 语句可以用在只允许表达式出现的地方,比如箭头函数、合并运算符和三元运算符等:
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
$callable = fn() => throw new Exception();
$nullableValue = null;
// $value 是非空的
$value = $nullableValue ?? throw new \InvalidArgumentException();
11、捕获异常而不存储到变量
PHP8 可以编写 catch (Exception) 代码来捕获异常,但是不用将其存储到一个变量里
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
$nullableValue = null;
try {
$value = $nullableValue ?? throw new \InvalidArgumentException();
} catch (\InvalidArgumentException) {
var_dump("Something went wrong");
}
运行结果:
string(20) "Something went wrong"
12、新增对注解的支持
注解是 PHP 8 引入的最大新特性之一,一开始理解起来可能有点困难(如果你有 Java 基础的话理解起来会相对简单)。
注解允许你添加元数据到 PHP 函数、参数、类等,这些元数据随后就可以通过可编程方式获取到,在 PHP 7 或者更低版本中实现这样的功能需要解析代码注释块,而通过注解可以直接访问深度集成到 PHP 自身。
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
// 首先,我们需要定义注解,注解本身只是一个原生的 PHP 类,并且自身被打上了注解的注释
#[Attribute]
class ApplyMiddleware {
public array $middlware = [];
public function __construct(...$middleware) {
$this->middleware = $middleware;
}
}
// 下面的语法会添加上述注解到 MyController 类,并且传入 auth 作为参数
#[ApplyMiddleware('auth')]
class MyController {
public function index() {
}
}
// 然后我们就可以在类中使用反射获取所有的 ApplyMiddleware 注解并读取给定的中间件参数
$reflectionClass = new ReflectionClass(MyController::class);
$attributes = $reflectionClass->getAttributes(ApplyMiddleware::class);
foreach ($attributes as $attribute) {
$middlewareAttribute = $attribute->newInstance();
var_dump($middlewareAttribute->middleware);
}
运行结果:
array(0) {
[0] => string(4) "auth"
}
13、新增构造函数属性提示支持
这个新特性是一个语法简写,支持将属性声明和构造函数属性初始化合并在一起
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
class User {
public function __construct(
public int $id,
public string $name,
) {}
}
$user = new User(1, 'Marcel');
var_dump($user->id);
var_dump($user->name);
运行结果:
int(1)
string(6) "Marcel"
14、Trait 支持定义抽象私有方法
declare(strict_types=1);
trait MyTrait {
abstract private function neededByTheTrait(): string;
public function doSomething() {
return strlen($this->neededByTheTrait());
}
}
class TraitUser {
use MyTrait;
// 支持该语法
private function neededByTheTrait(): string { }
// 不支持该语法 (错误的返回类型)
// private function neededByTheTrait(): stdClass { }
// 支持该语法 (非静态方法变成了静态方法)
// private static function neededByTheTrait(): string { }
}
14、新增对 match 表达式支持
match 表达式和 switch 分支语句类似,不过在语义上match表达式会更加安全并且可以直接返回值
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
echo match (1) {
0 => 'Foo',
1 => 'Bar',
2 => 'Baz',
};
运行结果:
Bar
15、引入了新的名为 mixed 的类型
该类型等价于 array| bool| callable |int |float |null |object |resource |string
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
function debug_function(mixed ...$data)
{
var_dump($data);
}
debug_function(1, 'string', []);
16、新增对 命名参数 的支持
命名参数允许基于参数名称传递参数到函数,而不是参数所在的位置。那么这样一来,函数参数就可以自解释了且与顺序无关,并且允许跳过默认值
示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
array_fill(start_index: 0, num: 100, value: 50);
17、新增对空安全运算符 ?-> 的支持
该运算符的左侧评估为 null 时,整个代码链路的执行就会被终止并且整体评估为 null。但是如果要不为 null ,那就要和普通的 -> 运算符功能一样 示例代码:
declare(strict_types=1);
class User {
public function getAddress() {}
}
$user = new User();
$country = $user?->getAddress()?->country?->iso_code;
var_dump($country);